Description
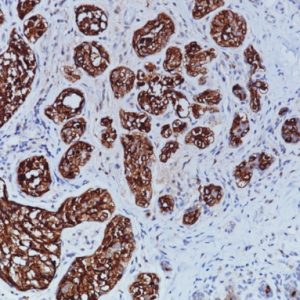
In normal epithelia, HMW Cytokeratins (CK5 and CK14) stain basal epithelia in the prostate gland.p63 is detected in prostate basal epithelial nuclei in normal prostate, however, is negative in malignant tumors of the prostate gland. Thus p63 is useful as a differential marker for benign and malignant tumors of the prostate gland and can be useful as a negative marker. Prostate – 2X can be used in combination with an additional antibody to generate a PIN-4 combination (see technical notes).
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
| WEIGHT | N/A |
|---|---|
| DIMENSIONS | N/A |
| INTENDED USE | IVD |
| SPECIES REACTIVITY | Human |
| SOURCE | Mouse Monoclonal |
| CLONE | XM26/LL002 + 4A4 |
| ISOTYPE | IgG1/kappa IgG3 IgG2a/kappa |
| ANTIGEN | CK5 CK14 p63 |
| LOCALIZATION | Cytoplasmic and nuclear |
| POSITIVE CONTROL | Normal prostate |
DATASHEETS & SDS
| Download Data Sheet |
| Download RUO Data Sheet for International |
| Download SDS Sheet |
Regulatory Notice: Biocare’s IVD-labeled products comply with US-FDA and European IVDD regulation. Other regions may have additional requirements for such labeling, please contact your local distributor.
REFERENCES
1. Moll R, et al. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultures cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11-24.
2. Yang Y, et al. differential expression of cytokeratin mRNA and protein in normal prostate, prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, and invasive carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1997 Feb;150(2):693-704.
3. Yang A, et al. p63, a p53 homolog at 3q27–29, encodes multiple products with transactivating, death-inducing, and dominant-negative activities. Mol Cell. 1998 Sep;2 (3):305-16.
4. Signoretti S, et al. p63 is a prostate basal cell marker and is required for prostate development. Am J Pathol. 2000 Dec;157(6):1769-75.
5. Tacha DE, Miller RT. Use of p63/P504S monoclonal antibody cocktail in immunohistochemical staining of prostate tissue. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2004 Mar;12(1):75-8. Biocare Medical, Walnut Creek, California.
6. Beach R, et al. P504S immunohistochemical detection in 405 prostatic specimens including 376 18-gauge needle biopsies. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002 Dec;26 (12):1588-96.
7. Luo J, et al. Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase: a new molecular marker for prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2002 Apr 15;62(8):2220-6.
8. Wang Y, et al. Cell differentiation lineage in the prostate. Differentiation. 2001 Oct;68(4-5):270-9.
9. Tokar EJ, et al. Stem/progenitor and intermediate cell types and the origin of human prostate cancer. Differentiation. 2005 Dec;73(9-10):463-73.
10. Collins AT, et al. Identification and isolation of human prostate epithelial stem cells based on alpha(2)beta(1)-integrin expression. J Cell Sci. 2001 Nov;114(Pt 21):3865-72.
11. Center for Disease Control Manual. Guide: Safety Management, NO. CDC-22, Atlanta, GA. April 30, 1976 “Decontamination of Laboratory Sink Drains to Remove Azide Salts.”
12. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Protection of Laboratory workers from occupationally Acquired Infections; Approved guideline-Third Edition CLSI document M29-A3 Wayne, PA 2005.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.