Description
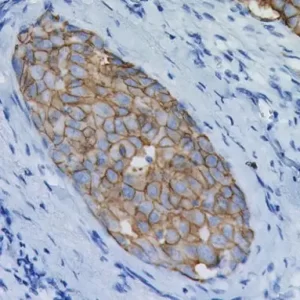
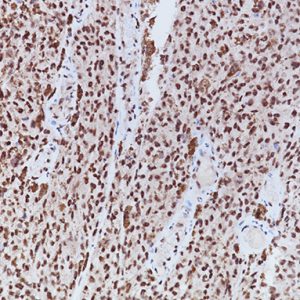
Placental Alkaline Phosphatase (PLAP) reacts with a membrane-bound isozyme (Regan and Nagao type) of PLAP occurring in the placenta during the 3rd trimester of gestation. This antibody is highly specific to PLAP and shows no cross-reaction with other isozymes of alkaline phosphatases. It is useful in the identification of testicular germ cell tumors and in separating thymic neoplasms from germ cell tumors. Unlike germ cell tumors, PLAP-positive somatic cell tumors uniformly express epithelial membrane antigen (EMA). PLAP may also be a useful marker in distinguishing classical seminoma from spermatocytic seminoma.
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
| WEIGHT | N/A |
|---|---|
| DIMENSIONS | N/A |
| INTENDED USE | IVD |
| SPECIES REACTIVITY | Human |
| SOURCE | Rabbit Monoclonal |
| CLONE | SP15 |
| ISOTYPE | IgG |
| ANTIGEN | Placental Alkaline Phosphatase (PLAP) |
| LOCALIZATION | Cell Membrane |
| POSITIVE CONTROL | Placenta or seminoma |
DATASHEETS & SDS
| Download Data Sheet |
| Download RUO Data Sheet for International |
| Download SDS Sheet |
Regulatory Notice: Biocare’s IVD-labeled products comply with US-FDA and European IVDD regulation. Other regions may have additional requirements for such labeling, please contact your local distributor.
REFERENCES
1. VI Shaw, et al. Utility of a selective immunohistochemical (IHC) panel in the detection of Components of mixed germ-cell tumors (GCT) of testis. United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology. Abstract #550. Annual Meeting, 1998.
2. Suster S, et al. Germ cell tumors of the mediastinum and testis: a comparative immunohistochemical study of 120 cases. Hum Pathol 1998 Jul;29(7):737-42.
3. Bailey D, et al. Immunohistochemical staining of germ cell tumors and intratubularmalignant germ cells of the testis using antibody to placental alkaline phosphatase and a monoclonal anti-seminoma antibody. Mod Pathol 1991. Mar;4 (2):167-71.
4. Burke AP, Mostofi FK. Placental alkaline phosphatase immunohistochemistry of intratubular malignant germ cells and associated testicular germ cell tumors. Hum Pathol 1988 Jun;19(6):663-70.
5. Center for Disease Control Manual. Guide: Safety Management, NO. CDC-22, Atlanta, GA. April 30, 1976 “Decontamination of Laboratory Sink Drains to Remove Azide Salts.”
6. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Protection of Laboratory workers from occupationally Acquired Infections; Approved guideline-Third Edition CLSI document M29-A3 Wayne, PA 2005.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.