Description
Programmed death 1 (PD-1) is a cell surface co-receptor in the CD28/CTLA-4 T-cell family and functions as a down regulator of the immune system through a dual mechanism of inhibition (1). PD-1 is expressed on the cell surface of activated T- and B-cells. Anti-tumor immunity may be controlled by the PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway. PD-L1, one of the ligands associated with PD-1, provides immunity for tumor cells by inducing apoptosis of activated T cells or by inhibiting cytotoxic T cells (1,2). Therapies that target the PD-1 receptor have shown unprecedented results with high levels of clinical response in patients with various cancer types (3). The presence of PD-1 positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) has been associated with poor prognosis in human breast cancers and may be useful in antibody therapy targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway (1). Treatments targeting PD-1 and its ligand, PD-L1, have also shown encouraging results in non-small-cell lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma and melanoma (4-6). This antibody can also be used in multiplex stains with CD8, FOXP3, CK8/18 and MART-1 mouse monoclonal antibodies.
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
| INTENDED USE | IVD |
|---|---|
| FORMAT | Predilute, VALENT |
| VOLUME | 20 ml, 6.0 ml |
| SOURCE | Rabbit Monoclonal |
| SPECIES REACTIVITY | Human; others not tested |
| LOCALIZATION | Cytoplasmic/cell membrane |
| ISOTYPE | IgG |
| ANTIGEN | A synthetic peptide corresponding to resides of human PD-1 protein |
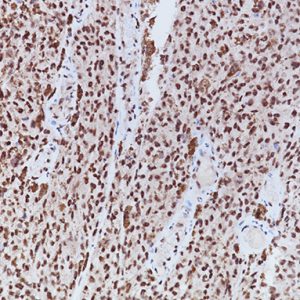
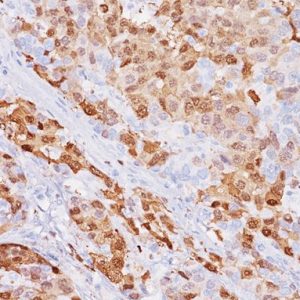
| POSITIVE CONTROL | Colon cancer and melanoma |
| CLONE | EP239 |
DATASHEETS & SDS
REFERENCES
1. Muenst S, et al. The presence of programmed death 1 (PD-1)-positive tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes is associated with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Jun;139(3):667-76.
2. Kim JW, Eder JP. Prospects for Targeting PD-1 and PD-L1 in Various Tumor Types. Oncology. (Williston Park). 2014 Nov;28(11 Suppl 3).
3. Tumeh PC, et al. PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature. 2014 Nov 27;515(7528):568 71.
4. D’Incecco A, et al. PD-1 and PD-L1 expression in molecularly selected non-smallcell lung cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2015 Jan 6;112(1):95-102.
5. Tykodi SS. PD-1 as an emerging therapeutic target in renal cell carcinoma: current evidence. Onco Targets Ther. 2014 Jul 25;7:1349-59.
6. Center for Disease Control Manual. Guide: Safety Management, NO. CDC-22, Atlanta, GA. April 30, 1976 “Decontamination of Laboratory Sink Drains to Remove Azide Salts.”
7. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Protection of Laboratory Workers from Occupationally Acquired Infections; Approved Guideline-Fourth Edition CLSI document M29-A4 Wayne, PA 2014.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.