SOPHiA DDM™ for Oncology
Everyone touched by cancer needs a clear path to the right care. We simplify complex data and reveal what matters most.
Genomic-powered precision medicine is at the forefront of innovation in cancer research. Advancements in next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology has brought about a new era of cancer care, furthering our understanding of disease mechanisms and therapeutic targets. However, with increasingly large and complex NGS data sets and multiple biomarkers, efficient and precise detection of relevant genomic alterations can be challenging
The SOPHiA DDM™ Platform removes the complexity from genomic analysis. Our algorithm-enabled bundle solutions empower data-driven decisions at all stages of the cancer care journey through a combination of accurate healthcare data analysis, intuitive interpretation functionalities, and secure knowledge sharing.
From confident analysis to relevant insights
SOPHiA DDM™ offers a streamlined workflow to annotate, interpret and report relevant NGS variants, minimizing complexity, thus increasing efficiency of your decision-making process.
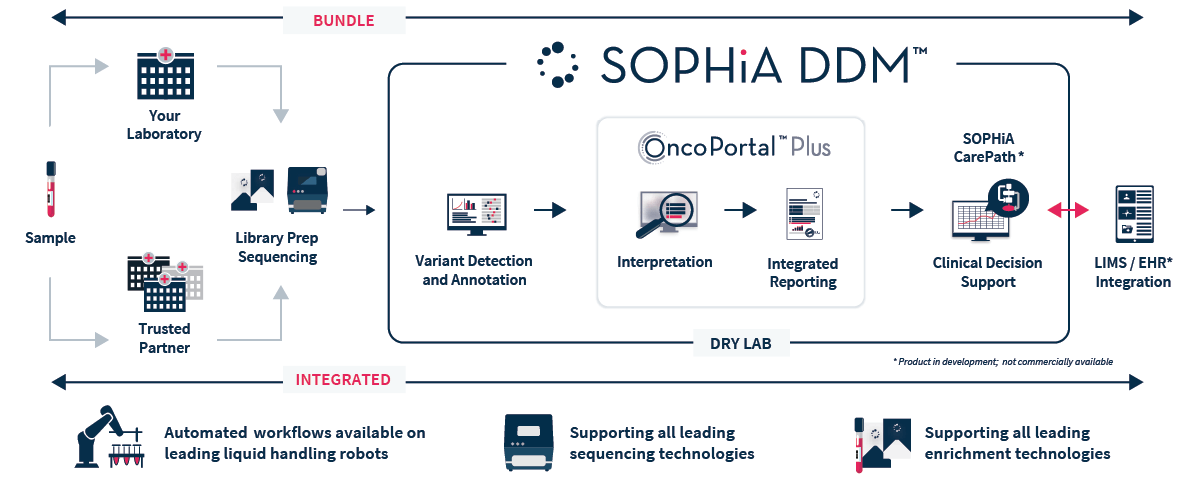
Knowledge at your fingertips
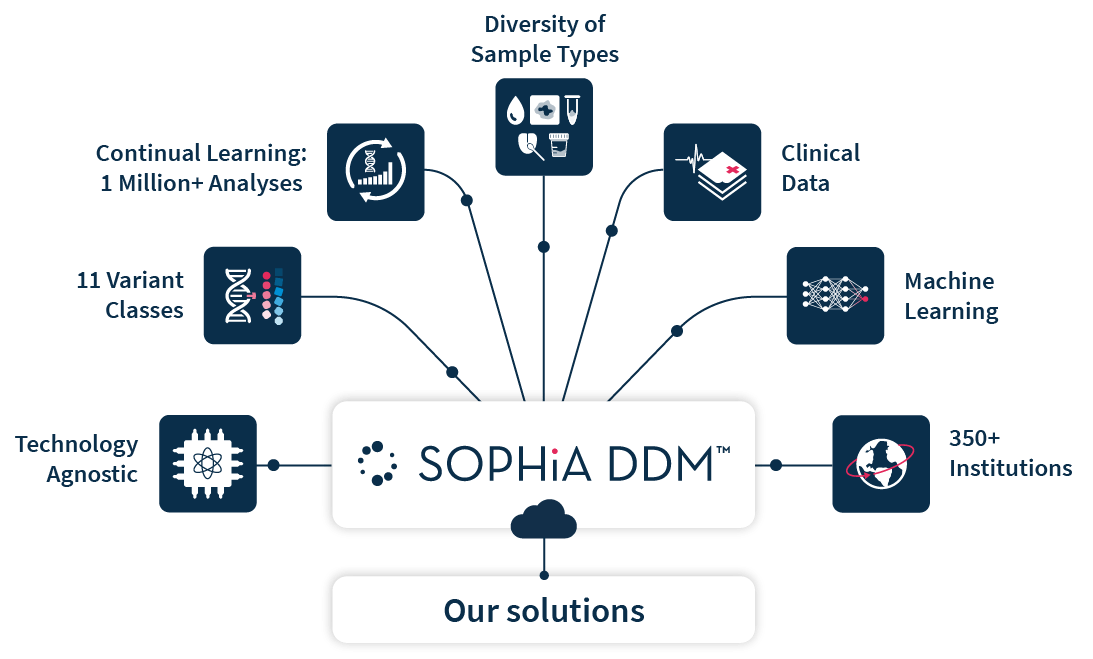
A decade of cumulative health data has been effectively analyzed in the SOPHiA DDM™ Platform, allowing us to leverage collective intelligence, machine learning, and pattern recognition to develop a breadth of solutions with finely tuned accuracy.
Solid Tumors
SOPHiA DDM™ for Solid Tumors analyzes complex variants and signatures with known involvement in solid tumors, yielding relevant decision-supporting information.
Blood Cancers
SOPHiA DDM™ for Blood Cancers allows detection of genomic biomarkers, delineating specific myeloid and lymphoid neoplasms.

Hereditary Cancers
SOPHiA DDM™ for Hereditary Cancers support rapid detection of known mutated hereditary cancer genes.
Our featured technology

Genomic Integrity Index
Our deep learning algorithm leverages low-pass whole genome sequencing data to reveal the extent of genomic scarring caused by homologous recombination deficiency (HRD).

RNAtarget Technology
An advanced customizable RNA-based sequencing approach that offers a single workflow with confident novel fusion detection, while also providing ability to detect SNVs/Indels and expression changes.

SOPHiA DDM™ for CGP
SOPHiA DDM™ combines analytical performance with streamlined interpretation of complex genomic variants, (including SNVs, Indels, CNVs, fusions, MSI and TMB), in the context of comprehensive genomic profiling (CGP).
Our featured technology

Radiomics
SOPHiA DDM™ for Radiomics offers imaging, end-to-end analytical solutions to help discover new biomarkers for disease evolution monitoring, treatment efficacy evaluation and therapeutic outcomes prediction.

Multimodality
To further advance precision medicine, we are pioneering the synergistic combination of radiomics, genomics and biological data. From biomarker discovery to patient stratification, we believe a multimodal approach holds a revolutionary potential for the future of precision medicine.
Next Generation Sequencing Providers in India
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) has emerged as a transformative technology in the field of genomics, enabling researchers and clinicians to decode the genetic information of individuals and organisms with unprecedented speed and precision. In India, NGS has gained significant momentum in recent years, thanks to a growing demand for genomic insights in various domains, including healthcare, agriculture, and biotechnology. This article explores the landscape of NGS providers in India, highlighting their contributions, capabilities, and the impact they are making on genomics research and clinical applications.
The Genomic Revolution in India
India, with its vast and diverse population, is poised to harness the potential of genomics to address critical healthcare challenges, unravel genetic diversity, and promote precision medicine. Next-generation sequencing has played a pivotal role in advancing these objectives. Several NGS providers in the country are instrumental in driving this revolution forward.
Impact on Healthcare
NGS providers in India have made substantial contributions to the healthcare sector. By offering NGS-based diagnostics and genetic counseling, they have enabled clinicians to diagnose and treat genetic disorders more effectively. Additionally, these providers have been instrumental in conducting large-scale genomic studies to understand the genetic basis of prevalent diseases in the Indian population.
Collaboration and Research
Many of these NGS providers actively collaborate with research institutions, universities, and hospitals to conduct cutting-edge research. They contribute to studies on population genetics, disease genomics, and pharmacogenomics, which are crucial for tailoring healthcare interventions to the Indian population.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the NGS landscape in India is promising, it also faces challenges. The high cost of NGS technology and data analysis, as well as the need for skilled personnel, remain significant hurdles. However, these challenges are being addressed through government initiatives, research grants, and capacity-building programs.
Next Generation Sequencing in oncology research in India
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) has revolutionized the field of oncology research in recent years. This advanced technology has allowed researchers to delve deeper into the genomic landscape of cancer, providing valuable insights into its causes, progression, and potential therapeutic targets. In this article, we will explore the various applications of NGS in oncology research and its role in advancing our understanding of cancer.
1. Genomic Profiling
NGS enables comprehensive genomic profiling of cancer samples, allowing researchers to identify mutations, copy number variations, and structural alterations in the tumor DNA. This information is crucial for characterizing the genetic heterogeneity of cancer and identifying potential driver mutations responsible for tumor initiation and progression.
2. Personalized Medicine
One of the most promising aspects of NGS in oncology is its role in personalized medicine. By sequencing a patient’s tumor DNA, researchers can identify specific genetic alterations that may be targeted with precision therapies, such as targeted therapies and immunotherapies. This approach minimizes the trial-and-error process associated with traditional cancer treatments, increasing the chances of successful outcomes.
3. Early Detection
NGS can also play a vital role in early cancer detection. Liquid biopsies, which involve analyzing circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in blood samples, can detect cancer-related mutations at an early stage when treatment options are more effective. This non-invasive approach is particularly valuable for monitoring cancer progression and treatment response.
4. Tumor Evolution
Cancer is a dynamic disease characterized by constant genetic changes within tumors. NGS allows researchers to track the evolution of tumors over time, helping to understand how they become resistant to treatments and identifying new therapeutic opportunities.
5. Biomarker Discovery
NGS facilitates the discovery of novel biomarkers associated with cancer. By analyzing large-scale genomic data from patient samples, researchers can identify genetic markers that predict prognosis, treatment response, and disease recurrence. These biomarkers can guide clinical decision-making and improve patient outcomes.
6. Functional Genomics
Beyond DNA sequencing, NGS technologies can be used to investigate other aspects of cancer biology, such as transcriptomics (gene expression), epigenomics (DNA methylation), and proteomics (protein expression). Integrating these data types provides a more comprehensive view of cancer biology and helps identify potential therapeutic targets.
7. Large-Scale Studies
NGS has made it possible to conduct large-scale genomic studies involving thousands of cancer patients. These studies, often referred to as “pan-cancer” analyses, aim to uncover commonalities and differences across various cancer types. Such research has led to the identification of shared pathways and potential therapeutic vulnerabilities.
8. Drug Development
NGS data is invaluable in drug development for oncology. Pharmaceutical companies use genomic information to identify and validate drug targets, stratify patients for clinical trials, and develop companion diagnostics to ensure the right patients receive the right treatments.
9. Data Integration
Integrating NGS data with clinical information, patient outcomes, and other omics data (such as proteomics and metabolomics) is a key challenge in oncology research. Advanced computational techniques are used to extract meaningful insights from these multidimensional datasets.
10. Ethical and Privacy Considerations
As NGS generates massive amounts of sensitive genomic data, ethical and privacy considerations are paramount. Researchers must adhere to strict data protection and informed consent protocols to ensure the responsible use of patient data.
Conclusion
Next-generation sequencing providers in India are at the forefront of the genomic revolution, propelling advancements in healthcare, agriculture, and research. Their dedication to pushing the boundaries of genomics and their contributions to understanding the genetic diversity of the Indian population are driving India towards a future where personalized medicine and genomics-based solutions become the norm. With continued investment in technology and talent, India is poised to make even greater strides in genomics in the years to come.
FAQ's on Next Generation Sequencing
What is Next Generation Sequencing (NGS), and why is it important in India?
NGS is a high-throughput DNA sequencing technology used to analyze genetic material. It is crucial for various applications in India, such as genomics research, clinical diagnostics, and agricultural studies.
How can I find NGS service providers in India?
You can search online, ask for recommendations from research colleagues, or consult academic institutions and biotechnology companies that offer NGS services.
What types of NGS services do providers in India typically offer?
NGS service providers in India offer a range of services, including whole-genome sequencing, exome sequencing, RNA sequencing, metagenomics, and more. They may also provide data analysis and bioinformatics support.
Are there any NGS providers in India with specific expertise in clinical genomics or diagnostics?
Yes, some NGS service providers in India specialize in clinical genomics and offer services for diagnosing genetic diseases and conducting pharmacogenomic studies.
How do I choose the right NGS service provider for my research or project?
Consider factors like the provider’s reputation, experience, turnaround time, pricing, quality control, and the specific NGS technologies and platforms they use.
What are the typical costs associated with NGS services in India?
Costs can vary widely based on the type of sequencing, depth of coverage, and the service provider. It’s best to request quotes from multiple providers for a precise estimate.
How can I ensure the data generated by an NGS service provider is of high quality?
You can inquire about the provider’s quality control measures, data analysis pipelines, and quality assurance protocols. References and reviews from other researchers can also be helpful.
Are there any regulatory considerations when using NGS services in India?
Depending on the nature of your research or project, you may need to adhere to ethical, regulatory, and data privacy guidelines. Check with the provider and relevant authorities for guidance.
Can NGS service providers in India assist with experimental design and data analysis?
Many NGS service providers offer consultation services to help researchers with experimental design and provide bioinformatics support for data analysis.
How do I contact NGS service providers in India for more information or to request a quote?
You can typically find contact information on the provider’s website or reach out to them through email or phone to inquire about their services and request quotes.
What is the significance of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) in oncology research in India?
NGS is crucial in oncology research in India as it enables the comprehensive analysis of cancer genomes, leading to better understanding of genetic mutations, personalized treatment options, and early detection strategies tailored to the diverse genetic profiles of Indian populations.
How can I access NGS services for oncology research in India?
To access NGS services, you can reach out to NGS service providers, research institutions, and clinical laboratories offering NGS-based tests. Many institutions in India have established collaborations for oncology research.
What are some common NGS-based tests used in oncology research in India?
Common NGS-based tests in Indian oncology research include whole-genome sequencing, whole-exome sequencing, targeted gene panel sequencing, and ctDNA analysis for liquid biopsies. These tests help identify cancer mutations and guide treatment decisions.
Are there specific genetic factors or mutations that are more prevalent in Indian cancer patients?
Yes, some genetic factors and mutations are more prevalent in Indian cancer patients due to genetic diversity. Researchers are actively studying these population-specific variations to develop targeted therapies and screening approaches.
What are the challenges associated with NGS-based oncology research in India, and how are they being addressed?
Challenges include cost constraints, data analysis expertise, and the need for regulatory frameworks. These challenges are being addressed through collaborations, skill development programs, and regulatory initiatives to ensure the responsible and effective use of NGS in oncology research in India.
Fill The form for More Information
24/7 HOUR AVAILABLE
+91 9871 206 667
